spinal cord compression diagnostic tests|spinal cord impingement vs compression : Brand Cervical myelopathy is a form of myelopathy that involves compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine (neck). Your cervical spine contains seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), with six intervertebral discs and eight nerve roots. 28 de ago. de 2023 · Agora que você conhece os critérios mais relevantes na hora de se registrar em uma plataforma, confira a nossa relação de melhores cassinos online para cada categoria: 📱 Melhor app de cassino Leo Vegas. 🎱 Melhor cassino para jogar bingo Betmotion. 🎁 Melhor cassino grátis Vbet. 🇧🇷 Melhor cassino no Brasil 1xBet.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Pilantra (Ao Vivo) lyrics | Tem gente que fala que ama, mas te deixa falando Tem gente que fala que volta, mas só Deus sabe quando Tem gente que passa a impres.
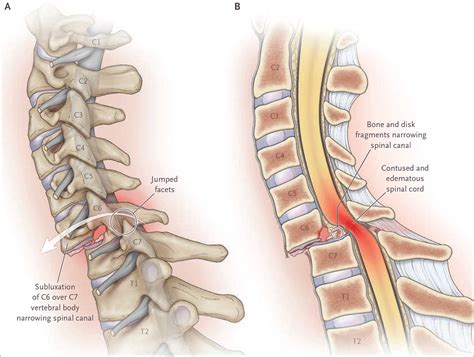
types of spinal cord compression
Various lesions can compress the spinal cord, causing segmental sensory, motor, reflex, and sphincter deficits. Diagnosis is by MRI. Treatment is directed at relieving compression. (See also Overview of Spinal Cord Disorders and . To accurately diagnose myelopathy, your healthcare provider will perform a thorough physical exam and order tests. These tests may include: Imaging tests, such as .Cervical myelopathy is a form of myelopathy that involves compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine (neck). Your cervical spine contains seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), with six intervertebral discs and eight nerve roots. The Hoffman test, also known as the Hoffman sign test, lets your doctor know whether there are compression — or pressure — problems in your spine near your neck.
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a neck condition that arises when the spinal cord becomes compressed — or squeezed — due to the wear-and-tear changes that occur in the spine as we age. Although the condition commonly . Diagnosing Spinal Cord Compression. To make a diagnosis, your healthcare provider will ask questions about your symptoms and do a complete physical exam. The exam will look for signs that indicate spinal compression, . Diagnosis. Treatments. Outlook. Prevention. What is spinal cord compression? Your spinal cord has nerves that send signals or messages back and forth between your brain and the rest of your.
Start New Search. ABOUT CAUSES DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT NEXT STEPS. What is spinal cord compression? Spinal cord compression is caused by any condition that puts pressure on your spinal cord. Your spinal cord is the .To diagnose cervical myelopathy, your doctor may: Conduct a physical examination and measure your muscle strength and reflexes. Conduct further tests, including an MRI scan, an X-ray or a CT myelogram of your neck. .Metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC) can happen when cancer grows and presses on the spinal cord. . This will help give an exact diagnosis. Lying flat. . If tests confirm you have MSCC, your healthcare team will decide what movement is safe and what you can and cannot do. You may be given a collar or brace to wear. This can help to . Spinal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the vertebral canal, which can occur at any level. The narrowing can compress on nerve tissue that travels through the spine and cause pain, often in the lower back or neck. Spinal stenosis most commonly occurs in the lumbar spine than the cervical spine. Studies have reported an incidence of 1 in 100 000 for cervical spine .
Heightened deep tendon reflexes in the knee and ankle are potential indicators of spinal cord compression and dysfunction. Clonus. Upon forcing the ankle to extend, the patient's foot rapidly beats up and down. . Since cervical stenosis with myelopathy is typically related to some sort of spinal cord instability, various diagnostic tests may .Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a neurologic condition that develops insidiously over time as degenerative changes of the spine result in compression of the cord and nearby structures. It is the most common form of spinal cord injury in adults; yet, its diagnosis is often delayed. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiology, natural history, . Learn about the causes and symptoms of spinal cord compression. This guide also looks at treatment options, when to contact a doctor, and more. Menu. Find a Doctor . Acute spinal cord compression is an emergency that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. Seek immediate medical help if you experience sudden symptoms of spinal cord .
The Hoffman test determines whether a person has spinal cord damage. During this quick test, you hold out one of your arms and open your palm facedown, extending your fingers in front of you. Doctors can diagnose spinal cord compression by performing a medical history and an exam, along with an X-ray of the spine and a CT scan or MRI test. Both a CT and MRI can provide a detailed image .
Initial evaluation of a patient with spinal stenosis often begins with a detailed history of symptoms and physical exam, with a focus on sensation, motor strength, reflexes, special tests, and gait. Stenosis in the cervical spine can lead to radicular symptoms due to nerve root compression and myelopathy due to spinal cord compression.
Cervical myelopathy describes a spinal cord compression at the cervical level of the spinal column resulting in spasticity (sustained muscle contractions), hyperreflexia, pathologic reflexes, digit/hand clumsiness, or gait disturbance.[1][2][3] Classically, it has an insidious onset, progressing in a stepwise manner with functional decline. Without treatment, .

Myelopathy is a disorder that results from severe compression of the spinal cord. The only way to treat the compression of the spinal cord is through decompression surgery. Causes of myelopathy include spinal stenosis, spinal trauma and spinal infections, as well as autoimmune, oncological, neurological and congenital disorders.
This guideline covers recognition, referral, investigation and management of spinal metastases and metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC). It is also relevant for direct malignant infiltration of the spine and associated cord compression. It aims to improve early diagnosis and treatment to prevent neurological injury and improve prognosisThey will do physical and neurological exams that include questions and tests to check how well the brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles are working. . The following imaging tests are used to diagnose spinal cord compression: MRI; CT scan; an x-ray of the spinal cord and spinal column (called myelography) Acute spinal cord compression (ASCC) is a surgical emergency requiring immediate neurosurgical treatment. Prognosis of the condition can vary and is most dependent on the time between diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we shall look at the risk factors, clinical features and management of acute spinal cord compression.Relief of compression. Treatment of spinal cord compression is directed at relieving pressure on the cord. Incomplete or very recent complete loss of function may be reversible, but complete loss of function rarely is; thus, for .
Spinal metastases are the most common tumors of the spine, comprising approximately 90% of masses encountered with spinal imaging. Spinal metastases are more commonly found as bone metastasis, although they are not limited to bone metastasis, and approximately 20% present with symptoms of spinal canal invasion and cord compression. .
treatment for spinal cord compression
Myelopathy is a term used to describe any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. It is usually due to compression of the spinal cord by osteophyte or extruded disc material. It is most commonly localized in the cervical spine but . Spinal fractures and injuries: Broken or dislocated bones in your vertebrae or near your spine can narrow your canal space. Inflammation from injuries near your spine can also cause issues. Spinal cysts or tumors: Growths within your spinal cord or between your spinal cord and vertebrae can narrow your spinal canal.
CT or plain radiographs may reveal traumatic injuries or other sources of spinal cord compression, but MRI is most commonly the test of choice for evaluation of acute spinal cord compression. 7 The appropriate consultant to treat acute spinal cord compression depends on the etiology. Most cases benefit from discussion with a spine surgeon, if . #### What you need to know Between five and 10 in every 200 patients with terminal cancer will have metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC) within their last two years of life. It is an oncological emergency.1 2 MSCC is caused by compression of the dural sac and its contents (spinal cord or cauda equina) by an extradural or intradural mass,3 and it . Spinal TB can include any of the following: progressive bone destruction leading to vertebral collapse and kyphosis, cold abscess formation (due to extension of infection into adjacent ligaments and soft tissues), spinal canal narrowing by abscesses, granulation tissue or direct dural invasion resulting in spinal cord compression and neurologic .To diagnose spinal cord compression, your healthcare provider will ask you questions about your symptoms and do a complete physical exam. During the exam, they will look for signs of spinal compression, such as loss of sensation, weakness, and abnormal reflexes. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
Malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) is caused by metastatic or direct tumour spread into the epidural space. Tumours affecting the spinal column are often classified by their location as extradural, intradural extramedullary, or intradural intramedullary. . Urgent diagnosis and treatment is essential to prevent irreversible spinal cord .To diagnose spinal cord compression, your healthcare provider will ask you questions about your symptoms and do a complete physical exam. During the exam, they will look for signs of spinal compression, such as loss of sensation, weakness, and abnormal reflexes. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.Common blood tests used in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected VO/SEA include: Complete blood count (CBC) with differential. . Because the morbidity associated with potentially delaying making a diagnosis of an acute spinal cord compression can be devastating, consider the risks and benefits before delaying CT myelography in .
Patel DA, Campian JL. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for patients with malignant epidural spinal cord compression. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Aug 10;18(9):53. 55. Abrahm JL, Banffy MB, Harris MB. Spinal cord compression in patients with advanced metastatic cancer: "all I care about is walking and living my life".

Bursting Tester exporters
WEBHearts Kartenspiel ⚡ kostenlos online spielen ⚡ ohne Anmeldung & Download + über 19600 Games ⭐️ Exklusive HTML5 & Highscore Spiele HIER!
spinal cord compression diagnostic tests|spinal cord impingement vs compression